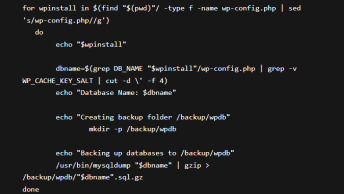
mysqldump command line tool is without doubt the most well known way to backup a MySQL database or multiple databases. Export options are text files containing multiple SQL statements or CSV files.
To dump an entire database simply connect to it using the right user/password combination and then select the database to be exported.
mysqldump -u [username] -p [database] > dump.sql
If you want to save the file as a .gzip (to save on disk space) then you should pipe it to gzip
mysqldump -u [username] -p [database] | gzip -3 > output_gzip.sql.gzYou can also dump one or multiple databases using the –databases followed by the database names:
mysqldump [options] --databases db_nameAnd to dump all databases you can use the –all-databases statement:
mysqldump [options] --all-databasesOr on Windows, because UTF-16 is not permitted as a connection character set so the dump file cannot be loaded correctly, use the --result-file option, which creates the output in ASCII format:
mysqldump -u [username] -p [database] --result-file=dump.sqlDumping a single table, or a selection of tables
To backup a single table or a selection of tables from a database use the following syntax:
- to export just the “foo” table from the “test_db” database:
mysqldump -u [username] -p test_db foo > dump1.sql
- and to export multiple tables, for example, “foo” and “bar” tables from the “test_db” database:
mysqldump -u [username] -p test_db foo bar > dump3.sql
Import back tables exported with mysqldump
To import tables back into the database simply use the following:
mysql -u [username] -p [database] < dumpfile.sql
Create a Script or CronJob for mysqldump
If you want to create a script or a cronjob that would use the mysqldump command you should create a .my.cnf file that contains your login details, for example:
[mysqldump]
user = my_mysql_username
password = my_passwordthen you can use that file in a script or cronjob:
mysqldump --defaults-file=/root/.my.cnf > output.sql