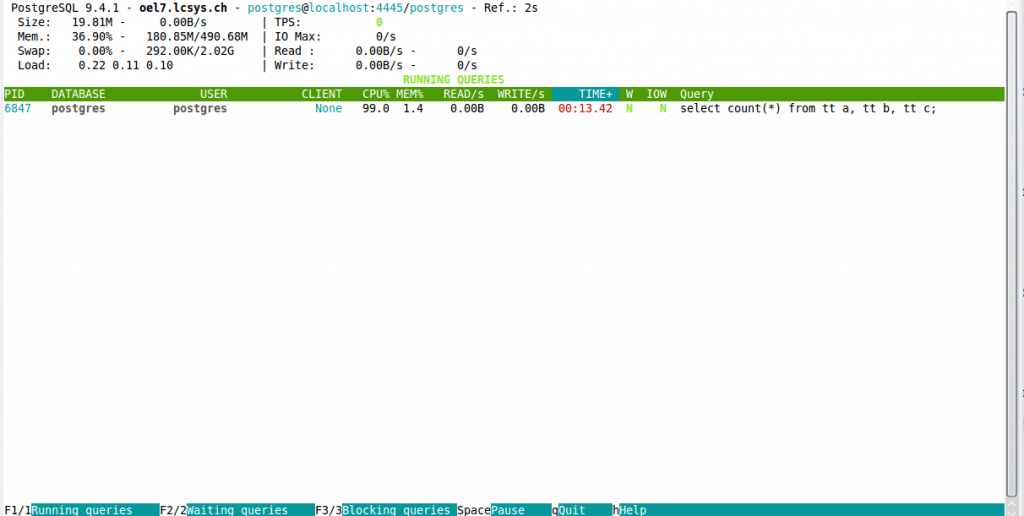
pg_activity is a great command-line tool for PostgreSQL server activity monitoring., and we are gonna show you how to install it and use it on a Linux machine. But what happens when someone that doesn’t have access to that Linux machine, wants to monitor the Postgre activity?
Well, you have several options available, you can use a python script on the server and share the information publicly available as a flask app, or, and this is what we are going to be overviewing in this article, you can use the built-in functionality of Pg_Admin.
pg_activity
As you may already know, pg_activity is a command tool for PostgreSQL server activity monitoring.
To install it you have to install the package psycopg2 from pgdg APT or YUM repositories. psycopg2 can also been installed from pip with pip install psycopg2 or pip install psycopg2-binary for the binary version.
After downloading and extracting the zip archive from github, you can do
sudo python setup.py installto install the pg_activity tool.
Once the tool is installed you can access it by running:
sudo -u postgres pg_activity -U postgrespgAdmin + adminpack
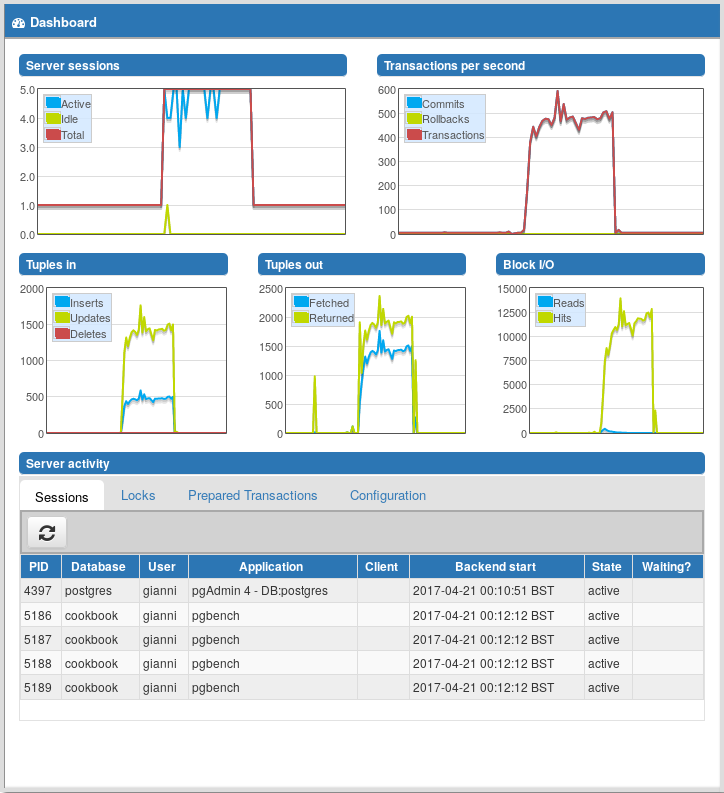
You can also use pgAdmin to get a quick view of what is going on in the database. For better control, you need to install the adminpack extension in the destination database, by issuing this command:
CREATE EXTENSION adminpack;This extension is a part of the additionally supplied modules of PostgreSQL. It provides several administration functions that PgAdmin can use in order to manage, control, and monitor a Postgres server from a remote location.
Once you have installed adminpack, connect to the database server; this will open a window similar to that shown in the following screenshot, reporting a general view plus information on connections, locks, and running transactions: