For logrotate we create a configuration file inside /etc/logrotate.d/ directory and check if there is a logrotate file in /etc/cron.hourly/ – if not copy it from cron.daily
Apache
EXAMPLE 1: logrotate file that will only rotate a single file when its size reaches 2000MB, keep 7 files compressed and delete them after a week.
/var/log/apache2/domlogs/domain.com-ssl* {
daily
missingok
notifempty
rotate 7
size 2000M
maxsize 2000M
maxage 7
dateext
compress
create
}EXAMPLE 2: Rotate all domlogs daily when they reach 200MB in size, keep 7 files rotated and delete them after a week. In this example, it is added that after rotation, httpd reload is performed, because otherwise Apache still writes to the same files after rotation.
/usr/local/apache/domlogs/* {
daily
missingok
notifempty
rotate 7
size 200M
maxsize 200M
maxage 7
dateext
compress
create
sharedscripts
postrotate
/usr/bin/systemctl reload httpd
endscript
}EXAMPLE 3: Rotate Apache error log every 12hours, keep max 30days
/var/log/apache*/access*.log {
missingok
notifempty
sharedscripts
copytruncate
rotate 12
daily
compress
delaycompress
maxage 30
postrotate if [ ! -f /usr/bin/systemctl ]; then ln -s ../init.d/*.service /usr/lib/systemd/system; fi
endscript
}MySQL
EXAMPLE 4: Rotate MySQL logs weekly and if MySQL is running then also flush logs.
/var/log/mysqld.log {
create 640 mysql mysql
notifempty
weekly
rotate 3
missingok
compress
postrotate
# just if mysqld is really running
if test -x /usr/bin/mysqladmin && \
/usr/bin/mysqladmin ping &>/dev/null
then
/usr/bin/mysqladmin flush-logs
fi
endscript
}Nginx
EXAMPLE 5: Rotate both Nginx access and error logs then reload nginx afterwards.
/var/log/nginx/access.log
/var/log/nginx/error.log {
size 1
missingok
notifempty
create 544 www-data adm
rotate 30
compress
delaycompress
dateext
dateformat -%Y-%m-%d-%s
sharedscripts
extension .log
postrotate
service nginx reload
endscript
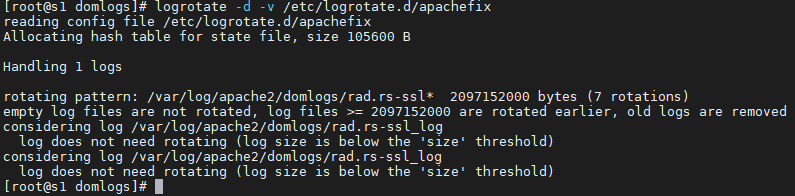
}after creating a file with the configuration (see examples above), we test logrotate with the command:
logrotate -d -v /etc/logrotate.d/apachefix- apachefix is file name
- -d flag is used for dryrun – files are NOT rotated but only shown what would be rotated
- –v flag stand for verbose – writes one line at a time what is/would be rotated
You can see more about the logrotate itself as well as additional information at the following link: https://linux.die.net/man/8/logrotate